CBS News
Ex-Mafia hitman sentenced to 25 years in prison killing of gangster Whitey Bulger

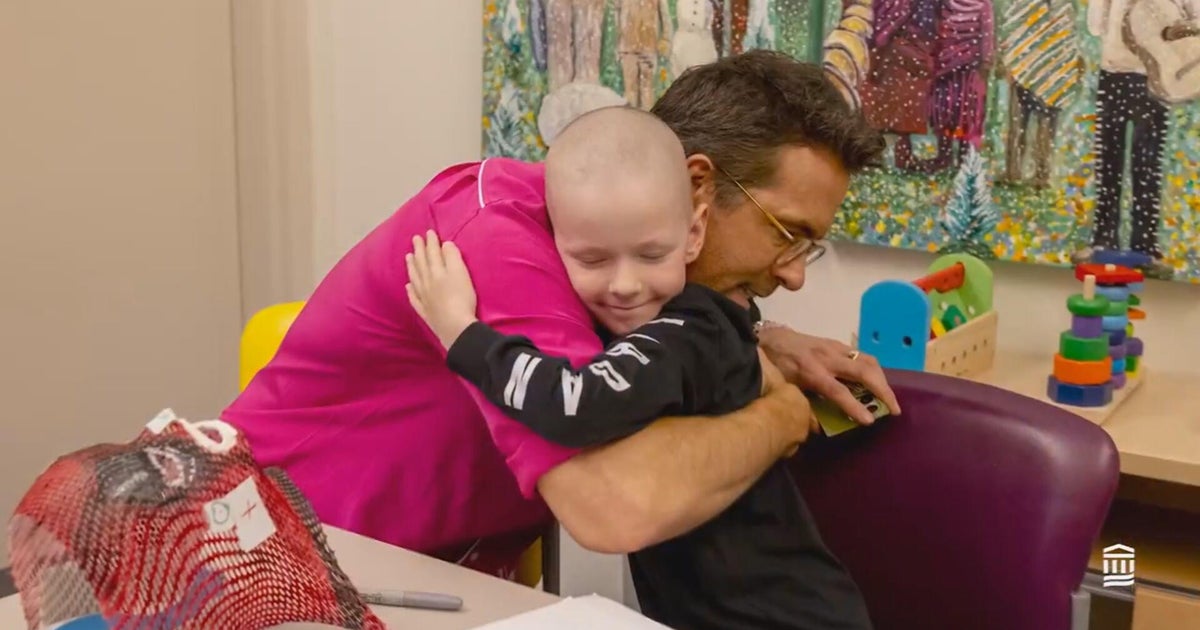
A former Mafia hitman was sentenced to 25 years in prison Friday in the 2018 fatal prison bludgeoning of notorious Boston gangster James “Whitey” Bulger.
Federal prisoner Fotios “Freddy” Geas was sentenced in federal court in northern West Virginia after pleading guilty to voluntary manslaughter and assault resulting in serious bodily injury.
Prosecutors initially had said Geas used a lock attached to a belt to repeatedly hit the 89-year-old Bulger in the head hours after he arrived at the troubled U.S. penitentiary, Hazelton, from another lockup in Florida in October 2018. Defense attorneys disputed that characterization, saying Geas hit Bulger with his fist.
Don Treeger /The Republican via AP
Geas, 57, already was serving a life sentence for previous violent crimes. The Justice Department said last year that it would not seek the death penalty against him in Bulger’s killing.
Bulger, who ran the largely Irish gang in Boston in the 1970s and ’80s, also served as an FBI informant who ratted on his gang’s main rival, according to the bureau. Bulger strongly denied ever being a government informant.
Bulger became one of the nation’s most wanted fugitives after fleeing Boston in 1994 thanks to a tip from his FBI handler that he was about to be indicted. He was captured at age 81 after more than 16 years on the run. Bulger was convicted in 2013 in a string of 11 killings and dozens of other gangland crimes, many of them committed while he was said to be an FBI informant.
(Photo credit: CBS News)
Another Hazelton prisoner, Massachusetts gangster Paul J. DeCologero, was sentenced to more than four years in prison in August on an assault charge in Bulger’s killing. Prosecutors said he acted as a lookout for Geas. A third inmate, Sean McKinnon, pleaded guilty in June to lying to FBI special agents. McKinnon was given no additional prison time and was returned to Florida to finish his supervised release. He had served a sentence for stealing guns from a firearms dealer.
According to court records, prisoners found out ahead of time that Bulger would be arriving at the West Virginia facility. DeCologero and Geas spent about seven minutes in Bulger’s cell during the attack.
A prisoner testified to a grand jury that DeCologero told him Bulger was a “snitch” and they planned to kill him as soon as he came into their unit.
Geas was a close associate of the Mafia and acted as an enforcer but was not an official “made” member because he is Greek, not Italian. He and his brother were sentenced to life in 2011 for their roles in several violent crimes, including the 2003 killing of Adolfo “Big Al” Bruno, a Genovese crime family boss in Springfield, Massachusetts. Another mobster ordered Bruno’s killing because he was upset that Bruno had talked to the FBI, prosecutors said.
Plea deals for Geas, DeCologero and McKinnon were disclosed May 13. Geas and DeCologero were identified as suspects shortly after Bulger’s death, but they remained uncharged for years as the investigation dragged on.
After the killing, experts criticized Bulger’s transfer to Hazelton, where workers had already been sounding the alarm about violence and understaffing, and his placement in the general population instead of more protective housing.
Bulger’s death was the result of multiple layers of management failures, widespread incompetence and flawed policies at the Bureau of Prisons, the U.S. Justice Department’s watchdog found in a 2022 report. The inspector general found no evidence of “malicious intent” by any bureau employees but said a series of bureaucratic blunders left Bulger at the mercy of rival gangsters.
(Image Credit: John Tlumacki/The Boston Globe)
That year, a federal judge dismissed a lawsuit filed by Bulger’s family against the bureau and 30 unidentified prison system employees.
In July, the U.S. Senate passed legislation to overhaul oversight and bring greater transparency to the bureau following reporting from The Associated Press that exposed systemic corruption in the federal prison system and led to increased congressional scrutiny.
CBS News
U.S. Marines, Japanese and Australian troops will train together amid heightened concerns over China
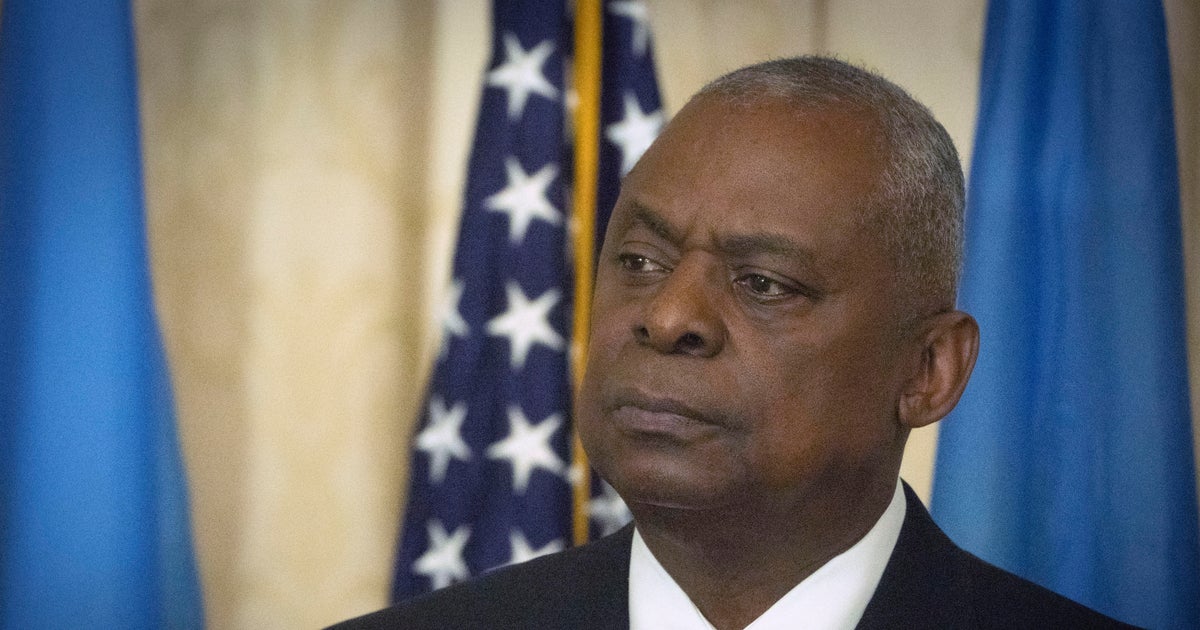

U.S. Marines will take part in joint training with Japanese and Australian forces in northern Australia, the three countries’ defense ministers announced Sunday as they expressed concern about a spate of confrontations with China’s increasingly assertive military.
Australia’s acting Prime Minister Richard Marles hosted U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin and Japanese Defense Minister Nakatani Gen for talks in Darwin, Australia.
The trilateral amphibious training between Australia, Japan and the U.S. Marine rotational force in northern Australia will begin in 2025 with Exercise Talisman Sabre. Australia will also join Exercise Orient Shield in Japan for the first time next year.
“Recognizing the critical role the trilateral partnership plays to uphold regional stability, we commit to trilateral policy coordination and to consult each other on regional security issues and contingencies,” they said in a joint statement.
In their statement, the three defense ministers reiterated “serious concern” about destabilizing actions in the East and South China seas including “dangerous conduct” by the Chinese military against Philippine and other vessels from the region. China claims the South China Sea almost in its entirety.
“We reiterate our strong opposition to any unilateral attempts to change the status quo by force or coercion,” they said, adding that it is “important that all states are free to exercise rights and freedoms consistent with international law.”
The ministers also urged the importance of peace and stability across the Taiwan Strait. China claims self-ruled Taiwan as its own territory and has stepped up military harassment with frequent drills around the island.
Marles, who is also Australia’s defense minister, said following talks with his Japanese counterpart in September that both nations looked to ways to build greater familiarity between their forces. One of the “obvious opportunities” was for Japan to participate in activities during the U.S. Marine rotation in Australia, he said Sunday.
“Having a more forward-leaning opportunity for greater training with Japan and the U.S. together is a really fantastic opportunity,” he said.
Asked if the increased military cooperation would anger Beijing, Marles said the decision was about building “the best relationships possible with like-minded countries, with our friends and with our allies.”
CBS News
Photographing the rooms of kids killed in school shootings
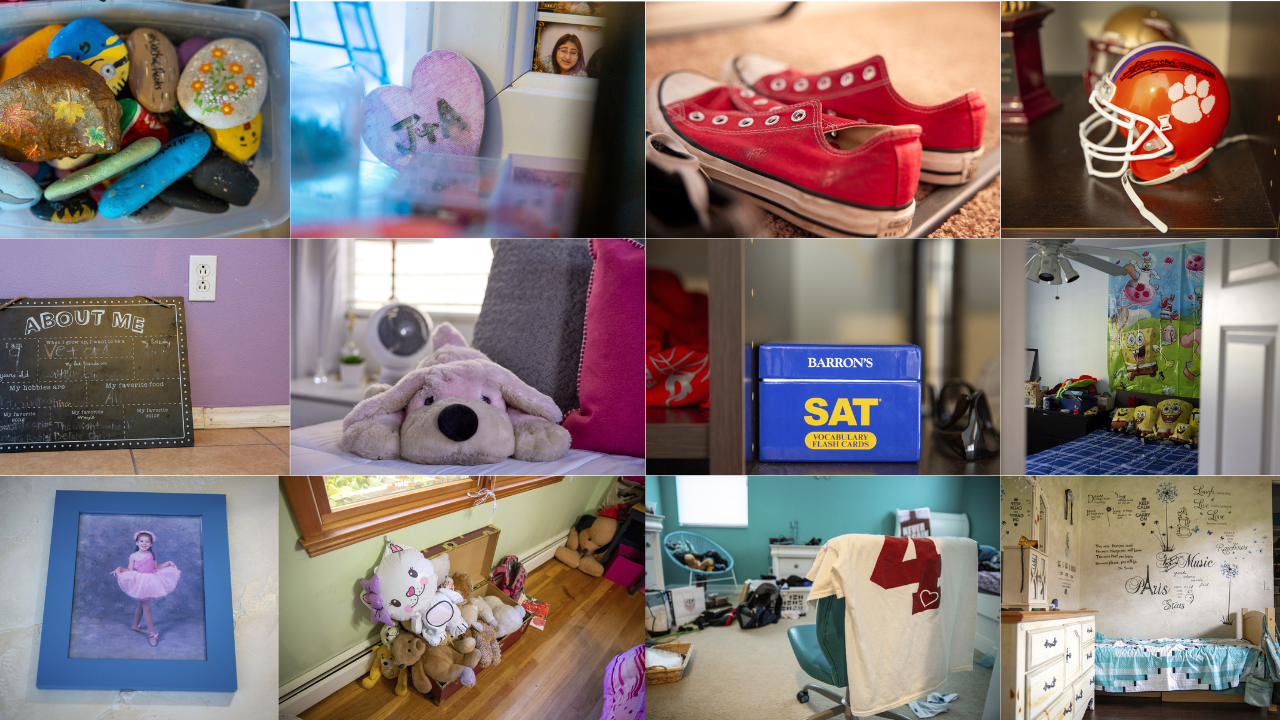

An unmade bed
A library book 12 years overdue
The next day’s outfit
Notes to her future self
Click on the door to enter
CBS News
How do you make a portrait of a child who isn’t there? Photographer Lou Bopp found a way, but it wasn’t easy.

In early 2018, I was deplaning after an 18-hour flight when Steve Hartman called. He had an idea: to photograph the still-intact bedrooms of kids who had been killed in school shootings.
It’s a headful. And six years later, I still don’t have an “elevator pitch” for the project — but then, I don’t often talk about this project. It is by far the most difficult I have ever worked on.
When Steve, my friend of about 25 years, asked me if I would like to be involved, I said yes without hesitation — even though I didn’t think we would get any families to agree. There is no way that I would have said no to partnering with him on this.
Emotionally, I was not sure how I would get through it. Within a few months I was on my way to Parkland, Florida. Alone. I’m not sure that I realized that I would be on my own.
But here I was. An on-location commercial photographer who focuses on people and pets to create compelling, honest, textural and connective moments for large brands, per my LinkedIn professional profile, on a project where there is no one to take photos of — for the most brutal of reasons.
How do you make a portrait of a child who is not there?
In each of these children’s rooms — the most sacred of places for these families — there was the sense that the child had just been there, and was coming right back. It was as if they’d just left their room like that when they went to school in the morning and were returning in the afternoon.
I wanted to capture that essence.
Most kids’ bedrooms are their very own special places, and these were no different. I looked everywhere, without touching anything. I photographed inside trash cans, under beds, behind desks. Their personalities shone through in the smallest of details — hair ties on a doorknob, a toothpaste tube left uncapped, a ripped ticket for a school event — allowing me to uncover glimpses as to who they were.
But there was an emotional challenge in addition to that creative one. Over the course of more than six years, we visited with many families around the country. The parents I spoke with seemed grateful that I was there. But each time I received a call or text from Steve about a new family, my heart sank.
It meant another family had lost a child.
I find it unfathomable that children being killed at school is even an issue. It makes no sense. It’s impossible to process. The night prior to each one of the family visits, I didn’t sleep. And I knew I wouldn’t going into the project. It’s not a self-fulfilling prophecy. It is nerves. And empathy. And sorrow. And fear.
In my notes from early on in the project, back in 2018, writing in seat 6H on the flight back from Nairobi, I reflected on the emotional task ahead.
“This is going to be one of the most difficult things ever, emotionally, for me, and not just work related. As I read my research documents, I get visibly emotional,” I wrote, noting my gratitude that the dark cabin prevented the other passengers from seeing me.
The prospect brought my own fears to the fore, both for myself — “I can’t help thinking about Rose,” my daughter, “and what if. I’ve lost sleep over envisioning the what-ifs well before Parkland” — and about and for meeting the families in the project: “When I read about April & Phillip and Lori’s plight, I somehow, for some reason put myself in their emotional position even though that is impossible, I have no idea, it’s beyond comprehension, I do not know what they feel. I do not know what I am going to say to them, I’m scared beyond belief. And alone.”
But just days later, I was photographing the first assignment for the project: Alyssa Alhadeff’s room. She was just 14 years old when she walked out of that room to head to Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School. I was shaky meeting the family friend who greeted me at the house. Her daughter was Alyssa’s best friend, and a photo of the two girls was on the table.
According to my notes, “The room was a beautiful teenager’s messy room. My emotions were kept in check the way that they usually are; By hiding behind the camera. I removed my shoes before entering. My heart was pounding and it reverberated through my body and soul, I felt like I was in one of the most sacred and special places on Earth. I was so careful not to touch anything.”
I left feeling ready to explode in sadness and anger.
Later that day, I photographed Carmen Schentrup’s room. Her younger sister had survived the Parkland shooting, but 16-year-old Carmen was killed in her AP Psychology class. Meeting her parents, April and Phillip, was what I was most scared of.
“I feel so much pain and compassion for them and I don’t want to say the wrong thing, drop cliches etc.,” I wrote at the time. “I spoke to Steve for guidance. He said, just be you. That’s all I can do. Just be me. He was right, those three words helped carry me through this entire project. Just be me.”
April let me in, and I worked quickly, only meeting Phillip as I was leaving. “The conversation felt like we all three were just trying to hold it together. I cannot imagine what they are going through, my heart hurts for them. This was / is such a painful project, and reconciling it will be impossible.
“I think about how anything can happen at any time to any of us. Literally. You never know,” I wrote.
After only about 16 hours on the ground in Florida, I was done with the first portion. I felt the project was a must, but I also dreaded the next call from Steve about the next family. I didn’t know when that call would come — many years later, or the very next day, possibly never.
But last month, we — and the documentary crew that filmed us working — completed this project. While I haven’t seen it yet, I know Steve’s piece won’t be a typical Steve Hartman segment. How could it be? I know he struggled too, and we both have spent a lot of time processing this.
I remember one August evening, I was devastated as I left the home of one of the families. Within minutes, I passed an ice cream shop crowded with other families — seemingly carefree, full of joy and laughter. The juxtaposition, mere minutes apart, cracked my soul.
I hope some way, somehow, this project can facilitate change — the only possible positive outcome for this I could comprehend. After the news cycle ends, these families will still be living with an incomprehensible nightmare.









