CBS News
Biden cancels $4.5 billion in student debt for over 60,000 public service workers

President Joe Biden on Thursday said an additional $4.5 billion in student debt is being canceled for about 60,000 teachers, nurses, firefighters and others, bringing the number of public service workers to get relief during his administration to more than 1 million.
More than $73 billion in loans have been forgiven under a 2007 initiative, according to an Education Department news release. Borrowers eligible for the latest round of relief should learn of their debt being cleared in coming weeks.
The borrowers getting relieved of debt are benefitting from reforms to the government’s Public Service Loan Forgiveness program. The PSLF program, signed into law by President George W. Bush in 2007, lets certain not-for-profit and government employees have their federal student loans canceled after 10 years of monthly payments. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau in 2013 estimated that a quarter of American workers might be eligible.
Less than 10,000 people received the relief intended by the program, which has been plagued by poor management and low acceptance rates.
The program “was so riddled by dysfunction that just 7,000 Americans ever qualified and countless public servants were trapped making payments on debts that should have been forgiven,” U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona said in a statement. “I want to send a message to college students across America that pursuing a career in public service is not only a noble calling but a reliable pathway to becoming debt-free within a decade.”
Helping those saddled with student debt was a main promise made by President Joe Biden in his 2020 campaign. But his efforts have been stymied by opposition including legal challenges, with the Supreme Court in 2023 voting 6-3 against Biden’s plan to erase the student debt of more than 40 million people. An alternative proposal is currently being blocked by a recent federal court ruling and a separate initiative called the “SAVE plan” was also temporarily blocked by a federal appeals court.
The outcome of the November presidential election could determine whether such programs survive, as the next administration would have the option of defending or ending the efforts, with Vice President and Democratic nominee Kamala Harris vowing to do the former.
Critics of the moves to forgive student debt include Republican nominee and former President Donald Trump. While in the White House, Trump’s 2020 budget proposal called for eliminating the loan forgiveness program for public employees.
CBS News
U.S. Marines, Japanese and Australian troops will train together amid heightened concerns over China
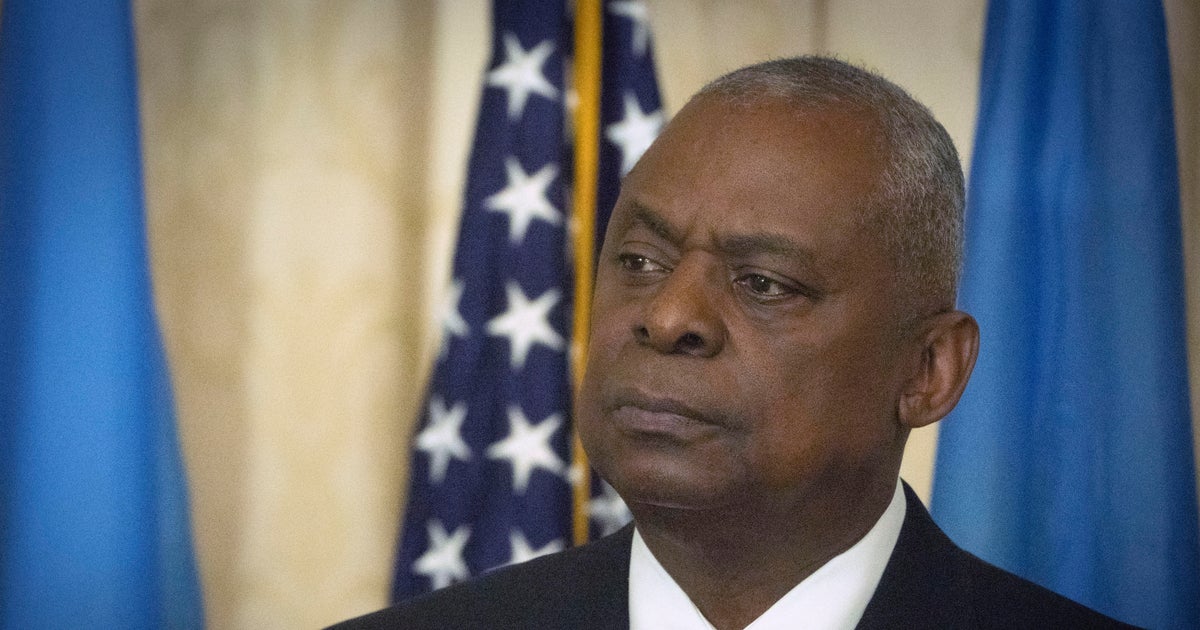

U.S. Marines will take part in joint training with Japanese and Australian forces in northern Australia, the three countries’ defense ministers announced Sunday as they expressed concern about a spate of confrontations with China’s increasingly assertive military.
Australia’s acting Prime Minister Richard Marles hosted U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin and Japanese Defense Minister Nakatani Gen for talks in Darwin, Australia.
The trilateral amphibious training between Australia, Japan and the U.S. Marine rotational force in northern Australia will begin in 2025 with Exercise Talisman Sabre. Australia will also join Exercise Orient Shield in Japan for the first time next year.
“Recognizing the critical role the trilateral partnership plays to uphold regional stability, we commit to trilateral policy coordination and to consult each other on regional security issues and contingencies,” they said in a joint statement.
In their statement, the three defense ministers reiterated “serious concern” about destabilizing actions in the East and South China seas including “dangerous conduct” by the Chinese military against Philippine and other vessels from the region. China claims the South China Sea almost in its entirety.
“We reiterate our strong opposition to any unilateral attempts to change the status quo by force or coercion,” they said, adding that it is “important that all states are free to exercise rights and freedoms consistent with international law.”
The ministers also urged the importance of peace and stability across the Taiwan Strait. China claims self-ruled Taiwan as its own territory and has stepped up military harassment with frequent drills around the island.
Marles, who is also Australia’s defense minister, said following talks with his Japanese counterpart in September that both nations looked to ways to build greater familiarity between their forces. One of the “obvious opportunities” was for Japan to participate in activities during the U.S. Marine rotation in Australia, he said Sunday.
“Having a more forward-leaning opportunity for greater training with Japan and the U.S. together is a really fantastic opportunity,” he said.
Asked if the increased military cooperation would anger Beijing, Marles said the decision was about building “the best relationships possible with like-minded countries, with our friends and with our allies.”
CBS News
Photographing the rooms of kids killed in school shootings
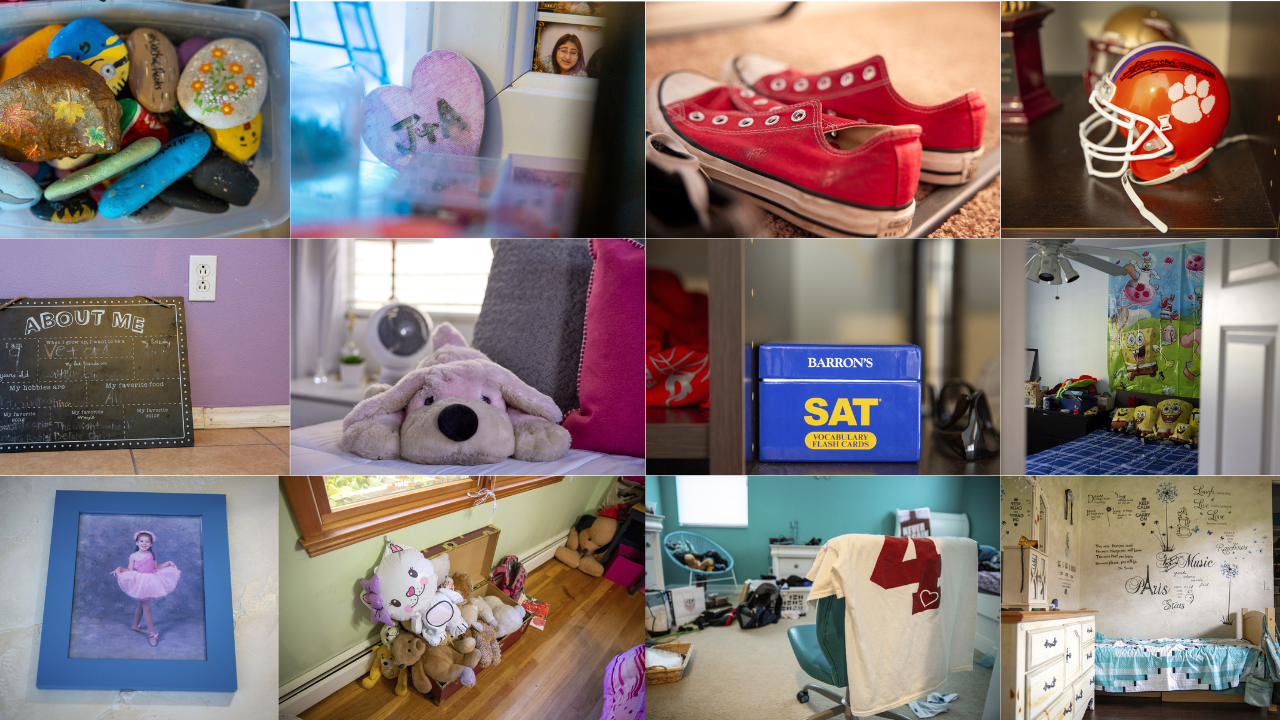

An unmade bed
A library book 12 years overdue
The next day’s outfit
Notes to her future self
Click on the door to enter
CBS News
How do you make a portrait of a child who isn’t there? Photographer Lou Bopp found a way, but it wasn’t easy.

In early 2018, I was deplaning after an 18-hour flight when Steve Hartman called. He had an idea: to photograph the still-intact bedrooms of kids who had been killed in school shootings.
It’s a headful. And six years later, I still don’t have an “elevator pitch” for the project — but then, I don’t often talk about this project. It is by far the most difficult I have ever worked on.
When Steve, my friend of about 25 years, asked me if I would like to be involved, I said yes without hesitation — even though I didn’t think we would get any families to agree. There is no way that I would have said no to partnering with him on this.
Emotionally, I was not sure how I would get through it. Within a few months I was on my way to Parkland, Florida. Alone. I’m not sure that I realized that I would be on my own.
But here I was. An on-location commercial photographer who focuses on people and pets to create compelling, honest, textural and connective moments for large brands, per my LinkedIn professional profile, on a project where there is no one to take photos of — for the most brutal of reasons.
How do you make a portrait of a child who is not there?
In each of these children’s rooms — the most sacred of places for these families — there was the sense that the child had just been there, and was coming right back. It was as if they’d just left their room like that when they went to school in the morning and were returning in the afternoon.
I wanted to capture that essence.
Most kids’ bedrooms are their very own special places, and these were no different. I looked everywhere, without touching anything. I photographed inside trash cans, under beds, behind desks. Their personalities shone through in the smallest of details — hair ties on a doorknob, a toothpaste tube left uncapped, a ripped ticket for a school event — allowing me to uncover glimpses as to who they were.
But there was an emotional challenge in addition to that creative one. Over the course of more than six years, we visited with many families around the country. The parents I spoke with seemed grateful that I was there. But each time I received a call or text from Steve about a new family, my heart sank.
It meant another family had lost a child.
I find it unfathomable that children being killed at school is even an issue. It makes no sense. It’s impossible to process. The night prior to each one of the family visits, I didn’t sleep. And I knew I wouldn’t going into the project. It’s not a self-fulfilling prophecy. It is nerves. And empathy. And sorrow. And fear.
In my notes from early on in the project, back in 2018, writing in seat 6H on the flight back from Nairobi, I reflected on the emotional task ahead.
“This is going to be one of the most difficult things ever, emotionally, for me, and not just work related. As I read my research documents, I get visibly emotional,” I wrote, noting my gratitude that the dark cabin prevented the other passengers from seeing me.
The prospect brought my own fears to the fore, both for myself — “I can’t help thinking about Rose,” my daughter, “and what if. I’ve lost sleep over envisioning the what-ifs well before Parkland” — and about and for meeting the families in the project: “When I read about April & Phillip and Lori’s plight, I somehow, for some reason put myself in their emotional position even though that is impossible, I have no idea, it’s beyond comprehension, I do not know what they feel. I do not know what I am going to say to them, I’m scared beyond belief. And alone.”
But just days later, I was photographing the first assignment for the project: Alyssa Alhadeff’s room. She was just 14 years old when she walked out of that room to head to Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School. I was shaky meeting the family friend who greeted me at the house. Her daughter was Alyssa’s best friend, and a photo of the two girls was on the table.
According to my notes, “The room was a beautiful teenager’s messy room. My emotions were kept in check the way that they usually are; By hiding behind the camera. I removed my shoes before entering. My heart was pounding and it reverberated through my body and soul, I felt like I was in one of the most sacred and special places on Earth. I was so careful not to touch anything.”
I left feeling ready to explode in sadness and anger.
Later that day, I photographed Carmen Schentrup’s room. Her younger sister had survived the Parkland shooting, but 16-year-old Carmen was killed in her AP Psychology class. Meeting her parents, April and Phillip, was what I was most scared of.
“I feel so much pain and compassion for them and I don’t want to say the wrong thing, drop cliches etc.,” I wrote at the time. “I spoke to Steve for guidance. He said, just be you. That’s all I can do. Just be me. He was right, those three words helped carry me through this entire project. Just be me.”
April let me in, and I worked quickly, only meeting Phillip as I was leaving. “The conversation felt like we all three were just trying to hold it together. I cannot imagine what they are going through, my heart hurts for them. This was / is such a painful project, and reconciling it will be impossible.
“I think about how anything can happen at any time to any of us. Literally. You never know,” I wrote.
After only about 16 hours on the ground in Florida, I was done with the first portion. I felt the project was a must, but I also dreaded the next call from Steve about the next family. I didn’t know when that call would come — many years later, or the very next day, possibly never.
But last month, we — and the documentary crew that filmed us working — completed this project. While I haven’t seen it yet, I know Steve’s piece won’t be a typical Steve Hartman segment. How could it be? I know he struggled too, and we both have spent a lot of time processing this.
I remember one August evening, I was devastated as I left the home of one of the families. Within minutes, I passed an ice cream shop crowded with other families — seemingly carefree, full of joy and laughter. The juxtaposition, mere minutes apart, cracked my soul.
I hope some way, somehow, this project can facilitate change — the only possible positive outcome for this I could comprehend. After the news cycle ends, these families will still be living with an incomprehensible nightmare.

