CBS News
Despite pressure on Sotomayor, Supreme Court unlikely to change before Trump takes office. Here’s why.
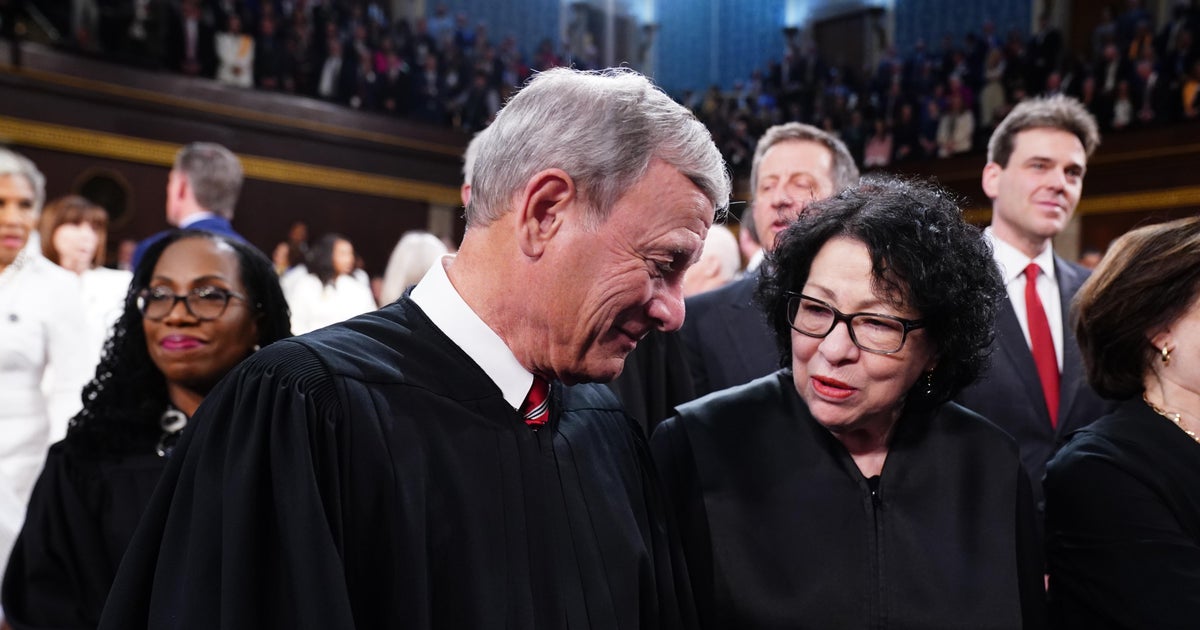
Washington — President-elect Donald Trump’s victory Tuesday has stirred up whispers about whether Justice Sonia Sotomayor should step down from the Supreme Court to allow President Biden to nominate a successor before Republicans take control of Washington.
But any changes in the composition of the nation’s highest court are unlikely in the coming months, even as lawmakers return for a lame-duck session to finish their business before Trump is sworn in for a second term and the GOP assumes the Senate majority.
Sotomayor hasn’t responded publicly to the chatter about a retirement, and she did not return a request for comment about her future. She remains an active questioner during oral arguments and has become known for biting dissents in hotly contested cases.
At 70, she is not the oldest member of the Supreme Court — Justice Clarence Thomas is 76 and Justice Samuel Alito is 74 — and she is newly into her tenure as the senior-most member of its liberal wing, a position she assumed following the retirement of Justice Stephen Breyer in 2022.
Sotomayor, the first Hispanic justice, is also a decade younger than Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg was when she faced pressure to step down from the Supreme Court in 2013 and 2014.
Ginsburg, who was treated for early-stage colon cancer in 1999 and pancreatic cancer in 2009, rejected any suggestion that she retire to allow then-President Barack Obama to name a successor while Democrats had control of the Senate. She remained on the Supreme Court until her death in September 2020, after which Trump, nearing the end of his first term, selected Justice Amy Coney Barrett to fill her seat. Barrett’s confirmation by the GOP-led Senate widened the Supreme Court’s conservative majority to 6-3.
With a second term for Trump on the horizon, and Democrats losing control of the Senate come January, when Republicans will hold at least 52 seats, progressives are fearful of a repeat of what happened with Ginsburg’s seat.
“We have no idea how long it will be until somebody who shares Justice Sotomayor’s jurisprudence, her values will be in a position to be nominated again,” Molly Coleman, executive director of the People’s Parity Project, a progressive judicial group, told CBS News. “Of course we all want to hope for the best, but unfortunately we’ve been left in a position where that’s all we can do.”
The circumstances of more than a decade ago are different from today, making it far from a sure thing that even if Sotomayor were to retire, the Senate would confirm her replacement before the GOP takes over. For one, Democrats currently have a narrow 51-49 majority, which includes the four independent senators who vote with the party.
One of those senators, Joe Manchin of West Virginia, told Politico in March that he would not support nominees who do not have GOP support.
“Just one Republican. That’s all I’m asking for. Give me something bipartisan. This is my own little filibuster. If they can’t get one Republican, I vote for none. I’ve told [Democrats] that. I said, ‘I’m sick and tired of it, I can’t take it anymore,'” Manchin, who is retiring from the Senate, said.
He later appeared to slightly reverse course, voting in September to advance the nomination of a candidate for a federal appeals court. A spokesperson for the senator told Axios at the time that Manchin learned opposition to the nominee was based on how the White House handled the process, not qualifications.
Erwin Chemerinsky, the dean of the University of California Berkeley Law School, said there is not enough time for a successor to be nominated and confirmed by the Senate by early January. Incoming House and Senate members will be sworn in on Jan. 3, and the results of the election will be reaffirmed by Congress on Jan. 6.
“Joe Manchin made clear he would not vote for any nominee without Republican support and no Republican would vote for a Biden nominee to replace Sotomayor. Sotomayor retiring now would likely just give Trump a vacancy to fill. It is totally different from whether Ginsburg should have retired in summer 2014 before the election,” he told CBS News in an email.
Chemerinsky wrote in September 2014 that Ginsburg should have retired that summer and warned her decision not to “could end up hurting her legal legacy.” Democrats had control of the Senate at that time, but lost it following the November 2014 midterm elections.
Even some progressive groups that called for open discussions about Sotomayor’s future on the court months ago are recognizing that the window has closed.
“The reality is it’s too late. It’s too late for Democrats to be having this conversation. It’s too late to be launching a pressure campaign. The ship has sailed,” Coleman, of the People’s Parity Project said.
She said discussions should have happened earlier this year and warned the consequences of waiting may be “catastrophic.”
Instead, liberal judicial advocacy groups are turning their focus to the confirming Mr. Biden’s remaining nominees to the federal district and appeals courts. There are currently 47 open seats on the federal bench, and 17 nominees are awaiting Senate action. There will be another 20 vacancies in the coming weeks, and 11 nominees are pending for those seats.
“Hand wringing about the unknown doesn’t help anyone right now,” said Maggie Jo Buchanan, managing director of the judicial group Demand Justice. “Right now, we are firmly focused on the fact that there are still 30 pending Biden nominees before the Senate that deserve, and need, confirmation. The Senate should be focused on working late, working weekends to get these talented individuals on the bench.”
Trump saw immense success with judicial confirmations during his first term, appointing 234 jurists to the Supreme Court, federal courts of appeals, district courts and U.S. Court of International Trade. But Mr. Biden is closing in on that number, with 213 appointments so far.
CBS News
Compromise deal reached at COP29 climate talks for $300 billion a year to poor nations

Countries agreed on a deal to inject at least $300 billion annually in humanity’s fight against climate change, aimed at helping poor nations cope with the ravages of global warming at tense United Nations climate talks in the city where industry first tapped oil.
The $300 billion will go to developing countries who need the cash to wean themselves off the coal, oil and gas that causes the globe to overheat, adapt to future warming and pay for the damage caused by climate change’s extreme weather. It’s not near the full amount of $1.3 trillion that developing countries were asking for, but it’s three times the $100 billion a year deal from 2009 that is expiring. Delegations said this deal is headed in the right direction, with hopes that more money flows in the future.
“Everybody is committed to having an agreement,” Fiji delegation chief Biman Prasad said as the deal was being finalized. “They are not necessarily happy about everything, but the bottom line is everybody wants a good agreement.”
It’s also a critical step toward helping countries on the receiving end create more ambitious targets to limit or cut emissions of heat-trapping gases that are due early next year. It’s part of the plan to keep cutting pollution with new targets every five years, which the world agreed to at the U.N. talks in Paris in 2015.
The Paris agreement set the system of regular ratcheting up climate fighting ambition as away to keep warming under 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The world is already at 1.3 degrees Celsius and carbon emissions keep rising.
Countries also anticipate that this deal will send signals that help drive funding from other sources, like multilateral development banks and private sources. That was always part of the discussion at these talks — rich countries didn’t think it was realistic to only rely on public funding sources — but poor countries worried that if the money came in loans instead of grants, it would send them sliding further backward into debt that they already struggle with.
“The $300 billion goal is not enough, but is an important down payment toward a safer, more equitable future,” said World Resources Institute President Ani Dasgupta. “This deal gets us off the starting block. Now the race is on to raise much more climate finance from a range of public and private sources, putting the whole financial system to work behind developing countries’ transitions.”
It’s more than the $250 billion that was on the table in the first draft of the text, which outraged many countries and led to a period of frustration and stalling over the final hours of the summit. After an initial proposal of $250 billion a year was soundly rejected, the Azerbaijan presidency brewed up a new rough draft of $300 billion, that was never formally presented, but also dismissed roundly by African nations and small island states, according to messages relayed from inside.
The several different texts adopted early Sunday morning included a vague but not specific reference to last year’s Global Stocktake approved in Dubai. Last year there was a battle about first-of-its-kind language on getting rid of the oil, coal and natural gas, but instead it called for a transition away from fossil fuels. The latest talks only referred to the Dubai deal, but did not explicitly repeat the call for a transition away from fossil fuels.
Countries also agreed on the adoption of Article 6, creating markets to trade carbon pollution rights, an idea that was set up as part of the 2015 Paris Agreement to help nations work together to reduce climate-causing pollution. Part of that was a system of carbon credits, allowing nations to put planet-warming gasses in the air if they offset emissions elsewhere. Supporters said a U.N.-backed market could generate up to an additional $250 billion a year in climate financial aid.
Despite its approval, carbon markets remain a contentious plan because many experts say the new rules adopted don’t prevent misuse, don’t work and give big polluters an excuse to continue spewing emissions.
“What they’ve done essentially is undermine the mandate to try to reach 1.5,” said Tamara Gilbertson, climate justice program coordinator with the Indigenous Environmental Network. Greenpeace’s An Lambrechts, called it a “climate scam” with many loopholes.
With this deal wrapped up as crews dismantle the temporary venue, many have eyes on next year’s climate talks in Belem, Brazil.
CBS News
GOP senator blocks promotion of general involved in Afghanistan withdrawal, sources say

The promotion of a three-star general who was part of the 2021 U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan has been paused by Republican Sen. Markwayne Mullin of Oklahoma, three sources familiar with the move confirmed to CBS News Saturday.
Lt. Gen. Christopher Donahue was slated to be promoted to a four-star rank and take command of the U.S. Army in Europe. However, he was not included in a batch of nearly 1,000 promotions that moved through the Senate Armed Services Committee this week despite receiving a Pentagon recommendation.
Mullin has put a hold on the promotion. The intention is to allow for the new Republican-controlled Congress and President-elect Donald Trump to weigh in on the promotion given Donahue’s involvement in the Afghanistan withdrawal, two sources familiar with the situation told CBS News.
Behind the scenes, there is an effort underway by the Army and other allies to convince Congress to move forward and lift the hold, which appears to be politically motivated, sources said.
ALLISON JOYCE/AFP via Getty Images
During the campaign, Trump frequently mentioned his surprise that no officers were consequently fired by President Biden for the chaotic withdrawal.
Military officers execute U.S. policy but do not create it. It was the Trump administration that in February 2020 brokered the deal with the Taliban to withdraw U.S. forces from Afghanistan, but it was Mr. Biden who decided to execute that withdrawal despite the Taliban breaking the terms of that U.S. agreement.
Donahue was the last U.S. soldier to exit Afghanistan in 2021. The U.S. evacuated about 125,000 people, including 6,000 Americans, over the course of its withdrawal, during which dozens of Afghans and 13 U.S. service members were killed in a suicide bombing outside Hamid Karzai airport in Kabul.
The U.S. underestimated the speed with which the Taliban would capture Kabul and the well-documented U.S. logistical and planning failures have been a focus of multiple internal probes at the Pentagon, State Department, and in Congress.
An extensive State Department report released last year found that “insufficient” planning, communication failures and an inability to grasp “the scale and scope of the operation” contributed to the chaotic operation.
CBS News has reached out to Mullin’s office but did not receive a response. It is not clear whether Trump is aware of the hold.
contributed to this report.
CBS News
Trump picks former White House aide Brooke Rollins to lead the USDA

President-elect Donald Trump said Saturday that he will nominate former White House aide Brooke Rollins to be his agriculture secretary, the last of his picks to lead executive agencies and another choice from within his established circle of advisers and allies.
The nomination must be confirmed by the Senate, which will be controlled by Republicans when Trump takes office Jan. 20, 2025. Rollins would succeed Tom Vilsack, President Biden’s agriculture secretary who oversees the sprawling agency that controls policies, regulations and aid programs related to farming, forestry, ranching, food quality and nutrition.
Rollins, who graduated from Texas A&M University with a degree in agricultural development, is a longtime Trump associate who served as his former domestic policy chief. She is president and CEO of the America First Policy Institute, a group helping to lay the groundwork for a second Trump administration.
Tom Williams/CQ-Roll Call, Inc via Getty Images
Rollins, 52, previously served as an aide to former Texas Gov. Rick Perry and ran a think tank, the Texas Public Policy Foundation.
Rollins’ pick completes Trump’s selection of the heads of executive branch departments, just two and a half weeks after the former president won the White House once again. Several other picks that are traditionally Cabinet-level remain, including U.S. Trade Representative and head of the Small Business Administration.
Trump didn’t offer many specifics about his agriculture policies during the campaign, but farmers could be affected if he carries out his pledge to impose widespread tariffs. During the first Trump administration, countries like China responded to Trump’s tariffs by imposing retaliatory tariffs on U.S. exports like the corn and soybeans routinely sold overseas. Trump countered by offering massive multibillion-dollar aid to farmers to help them weather the trade war.
President Abraham Lincoln founded the USDA in 1862, when about half of all Americans lived on farms. The USDA oversees multiple support programs for farmers; animal and plant health; and the safety of meat, poultry and eggs that anchor the nation’s food supply. Its federal nutrition programs provide food to low-income people, pregnant women and young children. And the agency sets standards for school meals.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr., Trump’s nominee to lead the Department of Health and Human Services, has vowed to strip ultraprocessed foods from school lunches and to stop allowing Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program beneficiaries from using food stamps to buy soda, candy or other so-called junk foods. But it would be the USDA, not HHS, that would be responsible for enacting those changes.
In addition, HHS and USDA will work together to finalize the 2025-2030 edition of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. They are due late next year, with guidance for healthy diets and standards for federal nutrition programs.










